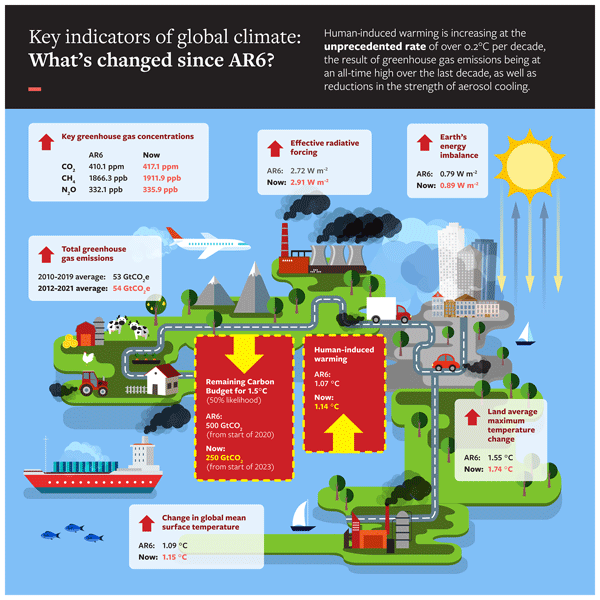
The greenhouse effect is a natural process essential to maintaining Earth’s climate, but human activities have amplified it, leading to significant environmental challenges. By understanding the mechanisms behind the greenhouse effect and the role of greenhouse gases, we can grasp how they contribute to global warming and climate change. This article explores the key contributors to the greenhouse effect, examines current trends in greenhouse gas emissions, and discusses strategies to mitigate their impact. By addressing these issues, we can work towards a sustainable future and reduce the risks associated with a warming planet.
Delve into this topic with gameslino.com for a comprehensive understanding.
1. Explanation of the Greenhouse Effect: Mechanism and Importance in Earth’s Climate System.
The greenhouse effect is a crucial process that governs Earth’s temperature, making it suitable for life. Sunlight reaches the Earth, with some of its energy absorbed by the surface, heating the planet. This absorbed energy is subsequently radiated back into space as infrared radiation. However, certain gases in the atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, capture a portion of this infrared radiation, preventing it from escaping. This trapped heat warms the planet, analogous to how a greenhouse warms the air within it.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying this natural process. This enhancement leads to global warming, which disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system, causing extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other significant environmental impacts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for addressing the climate crisis.
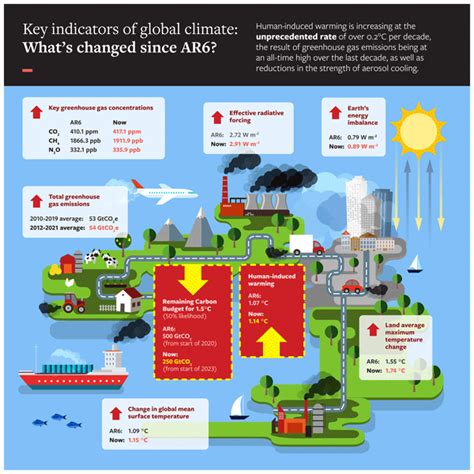
2. The Role of Greenhouse Gases: Key Contributors and Their Sources.
The greenhouse effect is a fundamental process that regulates Earth’s temperature, making it habitable for life. It begins when the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth, where some of it is absorbed by the surface, warming the planet. The Earth then emits this energy as infrared radiation back toward space. However, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap a portion of this infrared radiation in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space. This trapped heat warms the planet, much like a greenhouse warms the air inside.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying this natural process. This enhancement leads to global warming, which disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system, causing extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other significant environmental impacts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for addressing the climate crisis.
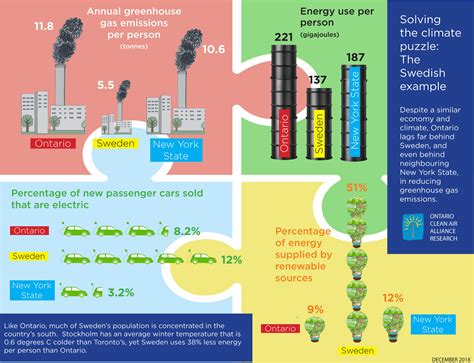
3. Impact of the Greenhouse Effect on Global Warming and Climate Change.
The greenhouse effect is a fundamental process that regulates Earth’s temperature, making it habitable for life. It begins when the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth, where some of it is absorbed by the surface, warming the planet. The Earth then emits this energy as infrared radiation back toward space. However, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap a portion of this infrared radiation in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space. This trapped heat warms the planet, much like a greenhouse warms the air inside.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying this natural process. This enhancement leads to global warming, which disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system, causing extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other significant environmental impacts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for addressing the climate crisis.

4. Current Trends in Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Data and Projections.
The greenhouse effect is a fundamental process that regulates Earth’s temperature, making it habitable for life. It begins when the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth, where some of it is absorbed by the surface, warming the planet. The Earth then emits this energy as infrared radiation back toward space. However, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap a portion of this infrared radiation in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space. This trapped heat warms the planet, much like a greenhouse warms the air inside.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying this natural process. This enhancement leads to global warming, which disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system, causing extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other significant environmental impacts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for addressing the climate crisis.
5. Strategies for Mitigating the Greenhouse Effect: Renewable Energy and Climate Policies.
The greenhouse effect is a fundamental process that regulates Earth’s temperature, making it habitable for life. It begins when the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth, where some of it is absorbed by the surface, warming the planet. The Earth then emits this energy as infrared radiation back toward space. However, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap a portion of this infrared radiation in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space. This trapped heat warms the planet, much like a greenhouse warms the air inside.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying this natural process. This enhancement leads to global warming, which disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system, causing extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other significant environmental impacts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for addressing the climate crisis.
Addressing the greenhouse effect and its impact on climate change is vital for safeguarding our planet’s future. By understanding its mechanisms, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and adopting sustainable practices, we can mitigate the effects of global warming. Collective action and innovative solutions are key to ensuring a healthier, more stable environment for generations to come.
gameslino.com